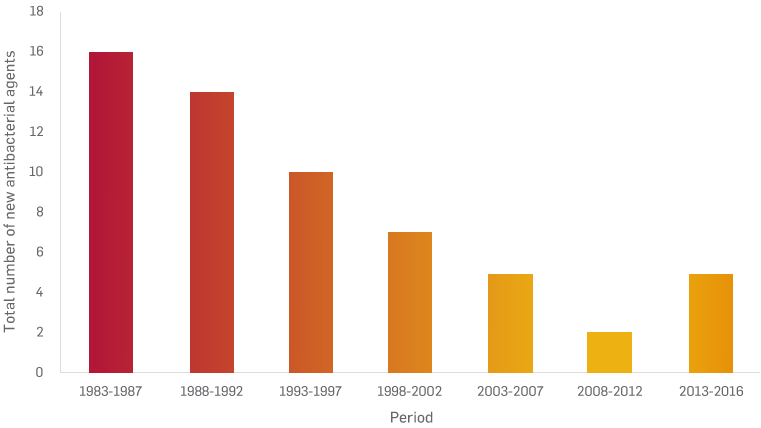Antibiotic development is dwindling1
Musculoskeletal infections, including infected non-unions, osteomyelitis and periprosthetic joint infections, are one of the biggest healthcare challenges of the 21st century.
As the rapid growth of antibiotic-resistant strains and biofilms continues to outpace the development of new antibiotics and antibiotic strategies, care delivery is becoming increasingly challenging and complicated.1,2
The global increase of infections caused by antibiotic resistant bacteria such as the ESKAPE pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas auruginosa, and Enterobacter species) requires targeted antibiotic treatment.
- In the EU, Norway and Iceland multidrug resistant (MDR) bacteria has an estimated economic loss of more than €1.5 billion each year.3
- In the USA, the cost of antibiotic-resistant infections to the health care system is $21 billion to $34 billion each year and more than 8 million additional hospital days.4
Surgical Site Infections
Surgical site infections (SSI) are a huge burden on hospital resources and annual expenditure.
- In England, SSI account for approximately 16% of all healthcare associated infections.5
- In the USA, SSI account for approximately 23% of hospital-acquired infections and cost up to $10 billion annually in direct medical expenses.6
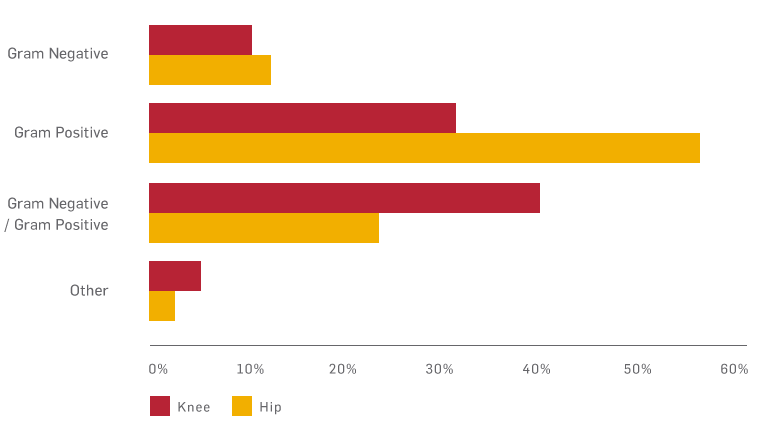
Identifying the micro-organisms that cause the SSI is essential to ensure the appropriate antibiotic and treatment strategies are selected.
Distribution of micro-organisms causing SSI7
Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI)
A major cause of arthroplasty failure, PJI often leads to multiple surgical interventions, prolonged antibiotic therapy and higher costs.
In England, the estimated total cost associated with treating deep wound infection in TKR and THR is c. £100,000 per patient.8
- 1% of primary hip and knee arthroplasties become infected.7
- 16% of hip revisions are carried out due to infection.9
- 23% of knee revisions are carried out due to infection.9
In the USA, the annual hospital cost of infected revisions is estimated to exceed $1.62 billion by 2020.10
Diabetic foot ulceration (DFU)
DFU is a major cause of lower-extremity amputations, with up to 24% of people with a DFU requiring amputation.11 Treatment for DFU carries considerable cost in terms of mortality and financial burden.
- It is estimated that 40% of amputations could be prevented with appropriate wound care.12
- Approximately 50% of patients who have foot amputations due to diabetes die within five years.13
- In the USA, amputations in adults with diabetes account for about 60% of the amputations of legs and feet not resulting from an injury.14
Choosing an innovative void management device to work alongside your infection management strategy is key to:
- Minimising avoidable complications
- Improving outcomes
- Reducing costs